Understanding the Honeymoon Phase in Type 1 Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes presents numerous challenges, but one that often brings a glimmer of hope is the honeymoon phase. This phase, a period of relative remission, can offer a respite from the daily demands of managing the condition. However, understanding this phase and knowing how to potentially extend it can significantly impact the long-term health and well-being of individuals with type 1 diabetes. This article delves into the intricacies of the honeymoon phase, offering insights into its nature, duration, and the strategies available to make the most of it. By gaining a deeper understanding, those affected can proactively manage their diabetes and improve their quality of life. The honeymoon phase is a critical period and understanding it is the first step toward effectively managing type 1 diabetes.
What is the Honeymoon Phase?
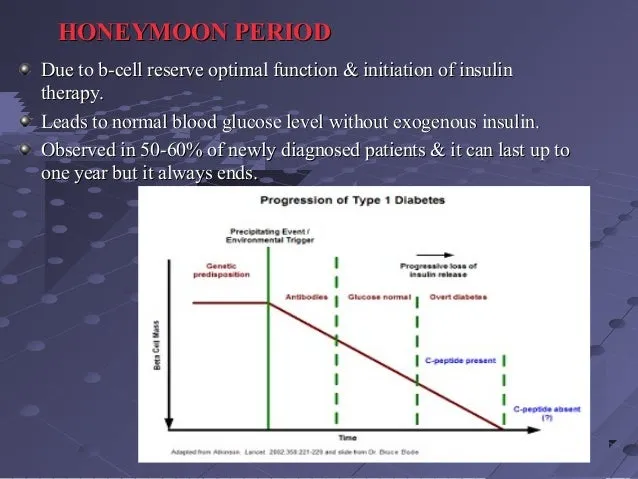
The honeymoon phase, also known as the remission phase, is a period that typically occurs shortly after the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. During this time, the bodyu2019s remaining insulin-producing cells, the beta cells in the pancreas, may still be functioning to some extent. This residual function results in reduced insulin requirements, often leading to a period where blood sugar levels are easier to manage with smaller insulin doses or even reduced medication. This phase varies in duration and intensity from person to person. It can last from a few weeks to several months, or even a year or more in some cases. The key is to recognize its significance and learn how to navigate it effectively to maximize its benefits.
Symptoms and Duration of the Honeymoon Phase

Recognizing the symptoms associated with the honeymoon phase is important for proper management. Common signs include a decreased need for insulin, improved blood sugar control with fewer fluctuations, and a reduced risk of hypoglycemia. The duration of this phase varies widely. Some individuals experience a honeymoon phase that lasts only a few weeks, while others may experience it for several months or even longer. Several factors influence the duration including the patient’s age, the initial severity of the diabetes, and the treatment plan implemented immediately after diagnosis. The sooner and more consistently aggressive interventions are started, the longer the honeymoon phase may last. Regular monitoring and consistent medical care are critical during this period.
Why is the Honeymoon Phase Important?
The honeymoon phase is an incredibly valuable time for individuals with type 1 diabetes. It offers several benefits that can significantly impact long-term health. During this phase, the reduced insulin needs and better blood sugar control lessen the daily burden of diabetes management, allowing for more flexibility and potentially reducing the risk of both short-term and long-term complications. Furthermore, this period gives individuals the opportunity to learn and adapt to diabetes management strategies with less immediate pressure. Effective management during the honeymoon phase can lead to better overall glycemic control, delaying the onset of chronic complications. The honeymoon phase is a window of opportunity to establish healthy habits.
Strategies to Extend the Honeymoon Phase
While the honeymoon phase is a natural phenomenon, there are several strategies that can potentially extend its duration and maximize its benefits. These strategies primarily focus on preserving the remaining beta-cell function and improving overall metabolic control. Implementing these methods requires a proactive approach and close collaboration with healthcare professionals. A comprehensive approach that includes medical management, lifestyle adjustments, and diligent monitoring will offer the best chance of extending the honeymoon phase and supporting long-term health.
Intensive Insulin Therapy

Initiating intensive insulin therapy early after diagnosis is a key strategy to preserve beta-cell function. This approach involves using multiple daily injections (MDI) or an insulin pump to mimic the body’s natural insulin release. By tightly controlling blood sugar levels from the outset, the stress on the remaining beta cells is reduced, potentially slowing their destruction. The goal is to maintain near-normal blood sugar levels as much as possible, as this helps prevent the progression of the autoimmune process. The type and intensity of insulin therapy should be carefully managed by a healthcare professional. Close monitoring and adjustments are essential to avoid hypoglycemia and achieve the best results.
Dietary Management and Nutrition
Dietary choices play a critical role in diabetes management, especially during the honeymoon phase. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while minimizing processed foods and added sugars, can improve blood sugar control. Carbohydrate counting and consistent meal timing are essential for managing blood sugar fluctuations and reducing the workload on the remaining beta cells. Consulting with a registered dietitian or a certified diabetes educator (CDE) can help develop a personalized meal plan that addresses individual needs and preferences. This may include guidance on appropriate portion sizes, carbohydrate intake, and meal timing to optimize glycemic control and promote overall health. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels in response to different foods can help fine-tune dietary strategies.
Regular Physical Activity
Incorporating regular physical activity into the daily routine has numerous benefits for individuals with type 1 diabetes, including helping to extend the honeymoon phase. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, which allows the body to use insulin more effectively. This can reduce the amount of insulin needed and improve blood sugar control. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, combined with strength training exercises at least two days a week. It’s important to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to prevent both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Consulting with a healthcare provider to create a safe and effective exercise plan that is tailored to individual needs is crucial. Regular physical activity is a powerful tool.
Stress Management Techniques

Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Effective stress management techniques are essential for maintaining good glycemic control and potentially extending the honeymoon phase. Chronic stress leads to the release of hormones like cortisol, which can raise blood sugar levels and make insulin resistance worse. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being. Adequate sleep, a balanced diet, and regular physical activity also contribute to stress reduction. Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and coping strategies. Finding healthy ways to manage stress is an important part of diabetes management.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
Frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels is critical for effective diabetes management and for maximizing the benefits of the honeymoon phase. Using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) or regularly testing blood glucose with a finger-prick meter provides valuable data to assess blood sugar trends and adjust insulin dosages or lifestyle factors. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, including an endocrinologist and a CDE, are also necessary to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. These healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance, identify potential issues, and optimize the management strategies. The data collected from monitoring informs decisions and adjustments, leading to better outcomes.
The Role of Medical Professionals
Managing type 1 diabetes, particularly during the honeymoon phase, requires a collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals. Building a strong relationship with a dedicated healthcare team provides the support and guidance needed to navigate the complexities of the disease. Regular visits, open communication, and adherence to their recommendations are crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes and extending the honeymoon phase.
Working with Your Endocrinologist

An endocrinologist, a specialist in hormonal disorders including diabetes, plays a central role in diabetes management. The endocrinologist prescribes and manages insulin therapy, monitors blood sugar control, and adjusts the treatment plan as needed. Regular appointments allow the endocrinologist to assess overall health, address any complications, and provide guidance on lifestyle modifications. Consistent communication and a willingness to actively participate in the treatment plan are essential for successful management and extending the honeymoon phase. The expertise and guidance of an endocrinologist are invaluable.
Benefits of a Support System
Having a strong support system can significantly improve the quality of life and diabetes management. This support may come from family, friends, support groups, or online communities. These networks provide emotional support, share experiences, and offer encouragement. Talking about the challenges and successes of managing type 1 diabetes with others who understand can reduce stress and improve motivation. Support groups and online communities offer a space to learn from others. Actively seeking and participating in a support system can greatly benefit those with type 1 diabetes and their families, improving overall well-being and helping extend the honeymoon phase. The support of others makes the journey of diabetes more manageable and less isolating.
Long-Term Benefits of Extending the Honeymoon Phase
Extending the honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes can provide numerous long-term benefits, enhancing overall health and quality of life. These advantages stem from improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of complications, and a greater sense of well-being. Proactive and consistent management during this crucial period can pave the way for a healthier future.
Improved Blood Sugar Control

Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is the cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Extending the honeymoon phase allows for better glycemic control, reducing the daily fluctuations and risks associated with high and low blood sugar. Consistent blood sugar levels minimize the long-term damage to blood vessels and organs. Improved control reduces the chance of developing both short-term and long-term complications. Monitoring blood sugar levels and adjusting treatment based on these results ensures optimal blood sugar control. Maintaining a balanced approach to diabetes care is necessary for improved blood sugar control.
Reduced Risk of Complications
Poorly managed type 1 diabetes can lead to serious long-term complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems. By extending the honeymoon phase, the risk of these complications is significantly reduced. Excellent blood sugar control minimizes the damaging effects of hyperglycemia on the body. Proactive diabetes management can delay or even prevent the onset of chronic complications, leading to a healthier and longer life. Early and consistent interventions, along with regular medical check-ups, are vital in reducing these risks. Taking action during the honeymoon phase provides the best opportunity to safeguard long-term health.
Enhanced Quality of Life
Living with well-managed type 1 diabetes significantly improves the quality of life. Extending the honeymoon phase reduces the daily burden of diabetes management, providing more flexibility and freedom. Improved blood sugar control translates to fewer blood sugar fluctuations. This leads to increased energy levels and reduced fatigue. The peace of mind that comes with knowing the condition is under control allows individuals to pursue their goals and enjoy a fuller life. Focusing on diabetes management is not just about health; it’s about the overall sense of well-being and the ability to live life to the fullest. Embrace this opportunity to create a positive and proactive approach to diabetes management.
Conclusion
The honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes is a unique opportunity to optimize diabetes management and improve long-term health outcomes. Understanding this phase, recognizing its benefits, and actively implementing strategies to extend it are crucial steps toward a healthier and more fulfilling life. By working closely with a healthcare team, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and prioritizing consistent blood sugar monitoring, individuals can make the most of the honeymoon phase, setting a strong foundation for a future. This proactive approach empowers individuals to take control of their health and live well with type 1 diabetes. Embracing these strategies allows for better management, improving both current and future health.
